In the market for a Data Integration is a leading manufacturer Informatica. This company is the first independent provider of data integration software. His best-known tool and the heart of his platform is Informatica PowerCenter, which has gone through many versions, and is a reference in the world of integration.
But apart from PowerCenter, Informatica also has other tools that focus on more specific purposes, while that are integrated into the platform, and always in the context of Data Integration.
The Informatica platform 9 is designed to cover the full life cycle data integration, which consists of five main steps: access, screening, cleaning, integration and delivery.
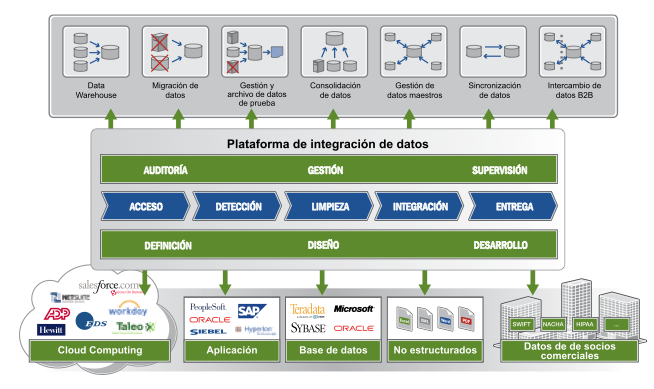
As usual with major software vendors, Informatica has many products, options and issues, and may cost a bit to get an idea of what each one, and what we need and what does not for our needs, but the fact that Informatica is an independent provider dedicated exclusively to data integration software makes a big difference.
This article will give a review of the main products that make the Informatica platform in September, grouped by type of problem they solve, and will provide a brief description of each one.
Data Integration
Informatica PowerCenter
Informatica PowerExchange
Data Quality
Informatica Data Explorer
Informatica Data Quality
Informatica Identity Resolution
B2B Data Exchange
Informatica B2B Data Exchange
Informatica B2B Data Transformation
Lifecycle Management Information
Informatica Data Archive
Informatica Data Subset
Informatica Data Privacy
The Data Integration products are those with a more generic and, to make an analogy, we could compare with ETL tools from other manufacturers.
Informatica PowerCenter
It might be called the flagship of Informatica. Connect with a multitude of data sources in real time, batch capture or even changes in the data (CDC).
Like other ETL tools, to define and implement on these data the necessary changes and then distribute them to the destination system as appropriate.
PowerCenter I would emphasize ease of use of its visual development tools, efficiency, scalability, expandability and functionality by the purchase of options 'Extra' and integration with other applications of the platform.
There are three product editions, each designed to cover a type of requirements. They are the Standard Edition with the basic options, the Advanced Edition which incorporates more advanced options, and Real Time Edition, which is aimed at the integration of real time data.
Informatica PowerExchange
This tool allows direct access, process and distribute data that are on platforms that often require intermediate steps to manage them with a standard ETL.
PowerExchange applications can connect to SaaS (Software as a Service), all kinds of databases, Email, LDAP, Web Services, XML, etc.
In an advanced version Complex Data Exchange can even work with complex data formats such as EDI, HL7, SWIFT, EDIFACT, etc.
With some of these platforms can work in real time, or even use the technology CDC (Change Capture), which detects changes to data in a non intrusive and over-burdening the source system with unnecessary queries.
It also integrates with Informatica PowerCenter and Informatica Data Quality.
It is not necessary to comment much to define this group, all tools designed to give help in improving the quality of data companies are here.
Informatica Data Explorer
It is the data profiling tool Informatica. Allows easy profiling data at the column level, table and between tables, which he named Informatica Data Analysis in three dimensions that can work on complex data.
From the analysis and profiling are generated metadata, related sources and destinations, and create reports that let you control the whole process of data quality, the anomalies, weaknesses and improvements over time.
It also integrates with Informatica PowerCenter and Informatica DataQuality to view results, create mappings automatically, or display specifications for cleaning and processing of data.
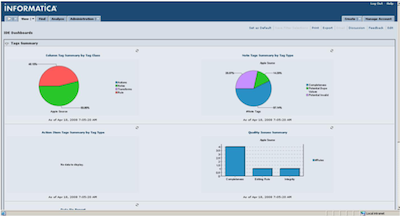
Informatica Data Quality
Data Quality has a broader scope than Data Explorer, is designed to manage the whole process of data quality, profiling, specification, cleaning, validation and monitoring, allowing him to participate in a coordinated manner both data analysts and developers and administrators . Each one has its own profile-oriented interface, and accessible in a web environment.
Its functionality is the possibility of defining rules and quality services that can be reused in different data quality projects.
It also has predefined rules to cleaning and geocoding addresses for more than 60 countries.
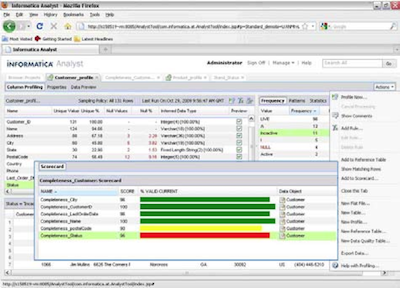
Informatica Identity Resolution
The identity resolution software to detect records that appear in the system as different individuals, but by the similarity between values associated with them can be deduced that correspond to the same identity. In other areas this process is called deduplication also customers, and can not miss on a data quality project.
Informatica Identity Resolution combines similarity comparison algorithms in an efficient manner, taking into account any typographical errors, changes in the data and even compares data in both languages and even different alphabets.
Processes can operate in both batch and real-time and has API's that allow detection features include identities other applications.
This group encompasses the tools that are used to facilitate data integration with other businesses, with the outside world, where the manner of access to information, standards and protocols change, and where it is vital to ensure the quality of incoming data, and not compromising the security of internal systems.
This product family, consisting of Informatica B2B Data Exchange and Informatica B2B Data Transformation is aimed at the effective exchange of information between enterprises, and offers great flexibility in terms of formats, allowing for both structured data and unstructured.
The tools are integrated with the rest of the Informatica platform, and external data collection also incorporate the necessary security measures that can be integrated seamlessly with internal data

Informatica B2B Data Transformation provides processing functions and data quality easy to use for the passage of external data to internal easy and no programming.
Informatica B2B Data Exchange can also define profiles internally and externally with business partners with which information is exchanged, so that on the same platform can define rules for transactions and expedite the protocol before the start of exchange .
It also manages events, current and historical and enables control of transactions.
The information has a lifecycle, and many data will become obsolete as time passes. Data will also be moved and replicated in different settings, some more critical than others, and efficient management of space is important. Many of the data need to be protected and managed to ensure that they can see them clear the appropriate profiles. It is important to manage the lifecycle of the information, and these are the Informatica tools provided to help with this task.
Informatica Data Archive
Informatica Data Archive is responsible for managing the archiving, with or without compression, inactive data, so stop using space and resources in major production systems, while still maintaining referential integrity and being accessible through tool and the various interfaces it provides.
Define rules and create metadata for data archiving, and provides direct connectivity to various databases, ERP and CRM systems, and even custom applications.
Another important feature is that by managing the archiving, to analyze and actively manage the data growth.
Informatica Data Subset
This application is used to create subsets of data from, for example, the full details of a production environment.
Allows you to define these subsets and policy creation and replication or maintenance of this data from the origin of the 'complete'. The software also is responsible for maintaining referential integrity within the data that form the subsets.
Includes accelerators for use on various ERP's, CRM's, and can greatly facilitate the creation and maintenance of development environments of reduced size, and date.
Informatica Data Privacy
In conclusion, this application is responsible for centrally manage data masking that require it within the organization, helping to comply with data protection laws, prevent leaks of sensitive data, and facilitate the creation of environments 100% operational development, but not displaying critical data.
Define masquerade rules, and has different algorithms or ways to implement it, while ensuring consistency and integrity of the data masked. Note that by dissociation of masking allows data values, while maintaining the functionality and readability of the same.
As expected, it also incorporates accelerators applications including masking predefined rules to implement quickly on various ERP and CRM applications.

 EAI Product Evaluation
EAI Product Evaluation Integration Design
Integration Design Implementation
Implementation Migration and Upgrades
Migration and Upgrades Support and Maintenance
Support and Maintenance Testing
Testing Platform Implementation
Platform Implementation Process Modelling
Process Modelling Process Optimization
Process Optimization Support and Maintenance
Support and Maintenance Testing
Testing Single Sign On
Single Sign On Access Management
Access Management Provisioning, User life Cycle Management
Provisioning, User life Cycle Management Personalization
Personalization Workflow
Workflow Integration with BPM and Middlware
Integration with BPM and Middlware SOA Roadmap and Consulting
SOA Roadmap and Consulting ESB Implementation
ESB Implementation SOA Testing
SOA Testing Service Creation
Service Creation Service Extraction
Service Extraction Service Utilization and Management
Service Utilization and Management